RSA
1976年,Diffie和Hellman在其著名论文,New Directions in Cryptography[1]中提出了公钥密码学Public-Key Cryptography的概念,并指出PKC需要满足两个需求,一是在不安全信道上完成密钥交换,另一个是要实现电子签名。为满足第一个需求,作者基于离散对数问题提出了Diffie-Hellman的密钥交换算法。但是,Diffie-Hellman不能实现电子签名。
1977年,Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, Leonard Adleman基于大数分解问题提出了RSA算法[2],能够同时支持密钥交换和电子签名。本文简单介绍下RSA公钥密码系统。
1 RSA算法
通常,一个密码学系统都包含三个算法,即{\(KeyGen\), \(Enc\), \(Dec\)},即密钥生成,加密,解密。
1.1 \(KeyGen\)
\(KeyGen(\tau)\rightarrow \{PK, SK\}\):
- 随机选择两个\(\tau\)-bit的素数\(p\), \(q\),计算\(n = pq, \phi(n)=(p-1)(q-1)\);
- 选取一个小于且与\(\phi(n)\)互素的整数\(e\),计算\(d\)使得\(ed \equiv 1\) mod \(\phi(n)\);
- \(PK=\{n, e\}, SK=\{n, d\}\)。
其中,\(\tau\)称为安全参数;欧拉函数\(\phi(n)\)表示小于等于\(n\)且与\(n\)互素的正整数个数,不难看出,对于semiprime(两个素数的积)\(n\),\(\phi(n)=(p-1)(q-1)\)。
1.2 \(Enc\)
\(Enc(m,PK)\rightarrow c\): \[ c = m^e\text{ mod }n \]
其中\(m\)是明文,\(c\)是密文。
1.3 \(Dec\)
\(Dec(c,SK)\rightarrow m\): \[ m = c^d\text{ mod }n \]
2 Correctness
RSA的正确性即: \[ m = Enc(Dec(m))\]
由\(ed \equiv 1\) mod \(\phi(n)\)及Euler定理(如果\(m\)与\(n\)互素,则\(m^{\phi(n)} \equiv 1 \text{ mod } n\))有
3 Security
RSA的安全性依赖于两个问题,factoring和RSA problem。目前还没有高效的算法解决这两个问题,但是这两个问题也没有被证明是困难的。
3.1 Factoring
如果能快速分解大整数\(n\),则显然能够求出私钥\(d\),RSA破解难度不会高于大数分解问题。
3.2 RSA Problem
RSA problem指在不直接计算\(d\)的情况下,能否解密,即已知\(c, n, e\)的情况下能否计算\(m\)。已知最高效的办法解RSA problem依然是先分解\(n\),所以RSA problem不会比factoring难,甚至可能更简单。
3.3 CPA and CCA secure
由于上面的RSA(textbook RSA)加密过程没有随机性,是确定性加密,不满足CPA-secure,自然也不满足CCA secure。Chosen Ciphertext Attack也很好构造,对于目标密文\(c=m^e\pmod{n}\),构造密文\(c^\prime=c\times(2)^e\pmod{n}=(2m)^e\pmod{n}\),解密后即得\(2m\)。
3.4 random padding
RSA通过random padding实现CPA-secure。PKCS#1v1.5中,加密前先将明文2-11Byte用非0随机数填充,然后再用RSA进行加密,解密反之。因为padding的存在,\(\tau\)-bit的key不能加密\(\tau\)-bit的明文,超过后要分成两个block分别加密。但是PKCS#1v1.5的random padding不是adaptive-CCA secure的。
4 Implementation
4.1 Multiprecision
如前所述,RSA密钥比较长,实现需要利用高精度库完成大数运算,如大数乘法,GCD(Euclidean算法),模逆(Extended-Euclidean算法),模幂(Square-and-Multiply method)等等。
4.2 \(\tau\)-bit primes generation
大素数生成采用重复生成伪随机数然后做素性测试直到获得一个素数。
4.3 Chinese Remainder Theorem
应用中国剩余定理(Chinese Remainder Theorem-CRT)可以加速解密过程。私钥\(SK=\{n,p,q,d_p,d_q,q_{inv}\}\),其中
\begin{align} d_p&=d\pmod{p-1} \\ d_q&=d\pmod{q-1} \\ q_{inv}&=q^{-1}\pmod{p} \\ \end{align}解密\(Dec(c)\rightarrow m\)如下:
\begin{align} m_1&=c^{d_p}\pmod{p} \\ m_2&=c^{d_q}\pmod{q} \\ h&=q_{inv}(m_1-m_2)\pmod{p}\\ m&=m_2+hq \end{align}相比\(n\), \(p,q\)的位数要小接近一半,模幂运算更快,解密能够加速近4倍。
5 Signature
由于RSA加密解密算法的对称性,RSA可以直接用来做电子签名,即:
\(Sign(m,SK)\rightarrow s\): \[ s = m^d\pmod{n} \]
\(Verify(s,PK)\rightarrow m\): \[ m = s^e\pmod{n} \]
其中\(m\)是明文,\(s\)是签名。
6 Benchmark
本部分给出rsa算法的性能数据,如下图
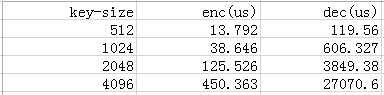
可见,\(KeyGen\)最慢,其次\(Dec\),\(Enc\)比较快,因为通常\(e\)比较小(65537)。
References
[1] W. Diffie, M. Hellman, New directions in cryptography, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory. 22 (1976) 644–654.
[2] R. Rivest, A. Shamir, L. Adleman, A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems, Communications of the ACM. 21 (1977) 120–126.